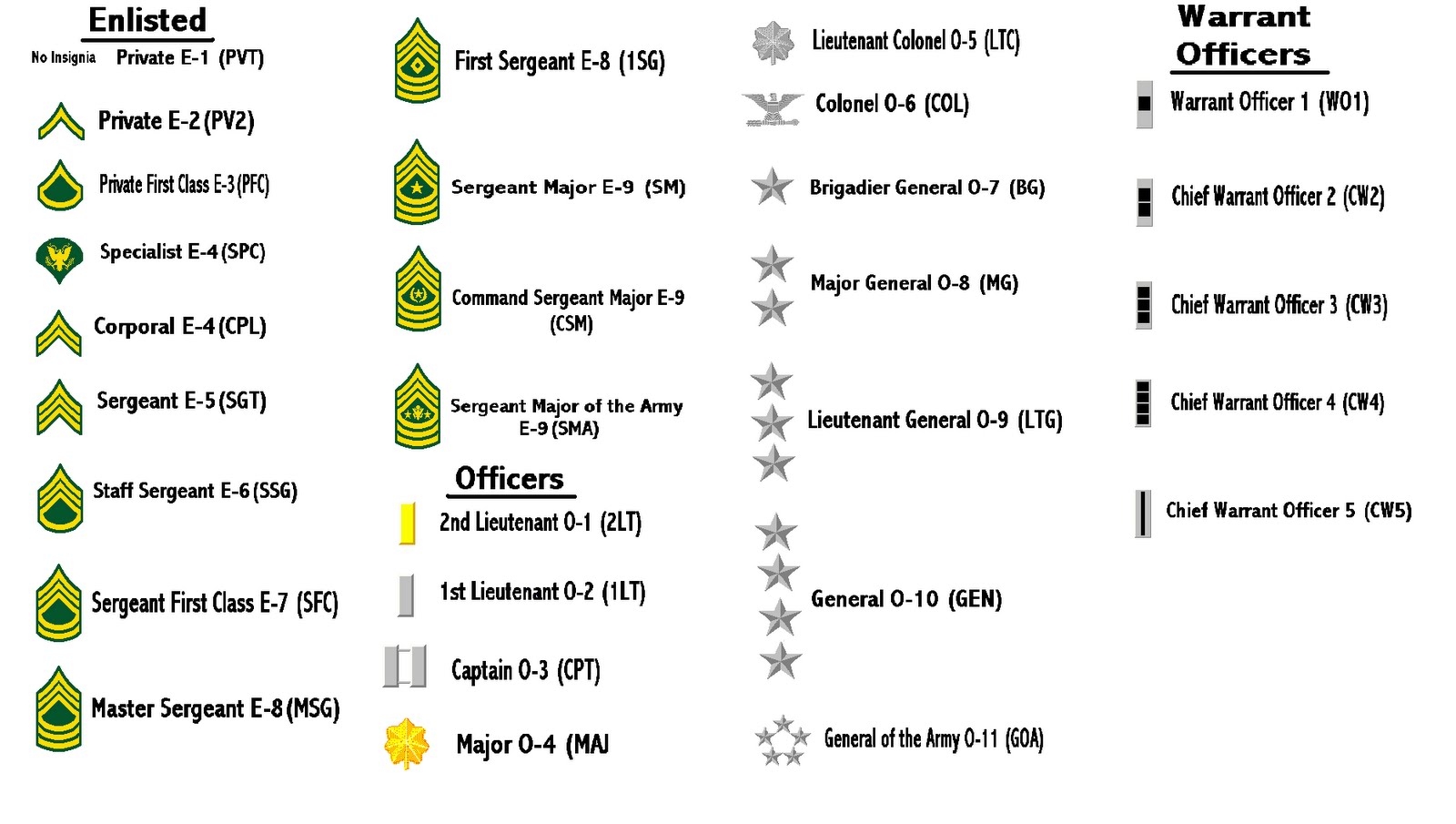
What is the significance of understanding "army ranks in order"? The military is a complex and hierarchical institution, and its ranks play a crucial role in maintaining order and discipline. Knowing the ranks from the lowest to the highest is essential for anyone interested in the military or considering a career in the armed forces. Each rank carries its own responsibilities, expectations, and privileges, and understanding this hierarchy provides insight into how military operations are organized and executed. Furthermore, it helps civilians appreciate the dedication and leadership skills required for each level within the military structure.
The military's rank structure is a time-tested system that ensures efficient command and control within the armed forces. It serves as a framework for leadership, accountability, and professional development. The ranks denote levels of authority and responsibility, from the junior enlisted personnel to the highest generals. This system not only establishes order but also fosters respect and discipline among service members. By exploring the army ranks in order, we delve into the nuances of military leadership and the path of career progression, revealing how each rank contributes to the overall mission and effectiveness of the military.
Understanding army ranks in order also helps bridge the gap between the military and civilian communities. It demystifies the chain of command and highlights the varied roles that service members play in safeguarding national security. Additionally, for those pursuing a career in the military, comprehending the rank structure is crucial for setting career goals and understanding the pathways to advancement. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different ranks, their roles, and the journey of progression through the military hierarchy. Whether you are a military enthusiast, a prospective recruit, or simply curious, this article aims to provide a clear and thorough understanding of army ranks in order.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Army Ranks
- The Enlisted Ranks: Building the Foundation
- Non-Commissioned Officers: The Backbone of the Army
- Warrant Officers: Technical Experts
- Commissioned Officers: Leaders and Commanders
- General Officers: Strategic Leadership
- Special Ranks and Titles
- Understanding Insignia and Symbols
- The Role of Military Education and Training
- The Path to Promotion: Advancing Through the Ranks
- The Importance of Leadership in the Military
- Comparing Army Ranks Globally
- FAQs About Army Ranks
- Conclusion: The Legacy of Military Ranks
- External Resources and Further Reading
Introduction to Army Ranks
The army ranks form the backbone of military structure and organization. They signify levels of authority, responsibility, and leadership within the military hierarchy. This system is vital for maintaining order, discipline, and command within the armed forces. From the lowest enlisted rank to the highest general, each level has specific roles and duties that contribute to the overall mission of the military. Understanding these ranks is not only important for those within the military but also for civilians who interact with military personnel or are interested in military affairs.
The concept of military ranks dates back centuries and has evolved over time to meet the changing needs of modern warfare. Each rank carries its own history, traditions, and significance, reflecting the values and priorities of the military as a whole. For those who serve, the rank structure provides a clear path for career advancement and personal development, offering opportunities for leadership and increased responsibility. For those outside the military, understanding the rank structure provides insight into the organization and functioning of the military, as well as the challenges and sacrifices faced by service members.
The hierarchy of army ranks is divided into several categories, each with its own set of ranks and levels of authority. These categories include enlisted ranks, non-commissioned officers, warrant officers, commissioned officers, and general officers. Each category plays a distinct role within the military, contributing to the overall effectiveness and success of military operations. By examining each category in detail, we gain a deeper understanding of the military rank structure and the roles and responsibilities associated with each level.
The Enlisted Ranks: Building the Foundation
Enlisted ranks form the foundation of military personnel. They are the backbone of the army, comprising the majority of service members who execute operational tasks and support missions. These ranks are essential to the day-to-day functioning of military units and operations. Enlisted personnel are typically responsible for carrying out orders, maintaining equipment, and performing specific duties critical to the success of missions.
The enlisted ranks are typically divided into junior enlisted and senior enlisted categories. The junior enlisted ranks include the entry-level positions that new recruits occupy when they first join the military. These ranks focus on training and developing the skills necessary for service members to perform their duties effectively. As enlisted personnel gain experience and demonstrate competence, they have the opportunity to advance to senior enlisted positions, which come with increased responsibilities and leadership roles.
The progression through enlisted ranks is based on time in service, performance, and completion of required training and education. Enlisted personnel are evaluated regularly and promoted based on their ability to meet the standards and expectations of their rank. This system encourages professional development and provides a pathway for individuals to advance their careers within the military. By understanding the enlisted ranks, we gain insight into the critical roles these service members play in maintaining the operational readiness and effectiveness of the military.
Non-Commissioned Officers: The Backbone of the Army
Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs) are often referred to as the backbone of the army, and for good reason. They are the leaders who bridge the gap between the enlisted personnel and the commissioned officers, providing guidance, mentorship, and supervision to junior service members. NCOs play a vital role in maintaining discipline, order, and morale within military units, ensuring that missions are executed effectively and efficiently.
NCOs typically hold ranks such as sergeant, staff sergeant, and sergeant first class, among others. These ranks come with significant responsibilities and authority, as NCOs are tasked with training and developing enlisted personnel, overseeing daily operations, and ensuring that military standards are upheld. NCOs are often the first line of leadership that enlisted personnel encounter, making their role crucial in shaping the character and capabilities of junior service members.
The path to becoming an NCO involves a combination of experience, training, and demonstrated leadership ability. NCOs are expected to lead by example, exhibiting the values and professionalism expected of military leaders. They are also responsible for fostering a positive and cohesive unit environment, addressing any issues or challenges that may arise, and ensuring that their subordinates are prepared for the demands of military service. By understanding the role of NCOs, we gain a deeper appreciation for the leadership and dedication required to maintain the effectiveness and success of military operations.
Warrant Officers: Technical Experts
Warrant officers occupy a unique position within the military rank structure, serving as technical experts and specialists in their respective fields. They are highly skilled individuals who provide critical expertise and support to military operations, often focusing on specific technical or tactical areas. Warrant officers play a vital role in ensuring that the military has the capabilities and knowledge necessary to execute complex missions and maintain operational readiness.
Warrant officers typically hold ranks such as warrant officer, chief warrant officer, and master warrant officer, among others. These ranks reflect their level of expertise and experience within their specialty. Warrant officers are often responsible for training and mentoring enlisted personnel and junior officers, sharing their knowledge and skills to enhance the overall capabilities of the military.
The path to becoming a warrant officer involves a combination of specialized training, experience, and demonstrated proficiency in a particular area. Warrant officers are selected based on their technical skills and ability to contribute to the success of military operations. They are respected for their expertise and are often called upon to provide guidance and support in challenging situations. By understanding the role of warrant officers, we gain insight into the specialized skills and knowledge that are essential to the success of military missions.
Commissioned Officers: Leaders and Commanders
Commissioned officers are the leaders and commanders within the military hierarchy, responsible for planning, executing, and overseeing military operations. They hold positions of authority and are tasked with making strategic decisions that impact the success of missions and the welfare of their personnel. Commissioned officers play a critical role in shaping the direction and effectiveness of the military, providing leadership and guidance at all levels of command.
The ranks of commissioned officers typically include second lieutenant, first lieutenant, captain, major, lieutenant colonel, colonel, and beyond. Each rank reflects a different level of responsibility and authority, with officers advancing through the ranks based on their performance, experience, and ability to lead. Commissioned officers are expected to exhibit the highest standards of professionalism, integrity, and leadership, serving as role models for their subordinates and ensuring that military objectives are achieved.
The path to becoming a commissioned officer typically involves completing a college degree, attending officer training programs, and demonstrating leadership potential. Officers are trained to manage complex operations, lead diverse teams, and make critical decisions under pressure. They are also responsible for fostering a positive and inclusive command climate, ensuring that their personnel are prepared for the challenges of military service. By understanding the role of commissioned officers, we gain a deeper appreciation for the leadership and dedication required to guide and command military forces effectively.
General Officers: Strategic Leadership
General officers occupy the highest ranks within the military hierarchy, providing strategic leadership and direction at the highest levels of command. They are responsible for overseeing entire military branches, formulating policies, and making decisions that impact national security and defense strategy. General officers play a critical role in shaping the future of the military and ensuring that it is prepared to meet the challenges of a rapidly changing world.
The ranks of general officers typically include brigadier general, major general, lieutenant general, and general. Each rank reflects a different level of authority and responsibility, with general officers advancing based on their experience, expertise, and ability to lead. General officers are expected to possess a deep understanding of military strategy, operations, and policy, as well as the ability to lead large and complex organizations.
The path to becoming a general officer involves a combination of experience, education, and demonstrated leadership ability. General officers are selected based on their ability to provide strategic vision and direction, as well as their commitment to the values and priorities of the military. They are respected for their leadership and are often called upon to provide guidance and support in challenging situations. By understanding the role of general officers, we gain insight into the strategic leadership and expertise that are essential to the success of military operations.
Special Ranks and Titles
In addition to the standard ranks within the military hierarchy, there are also special ranks and titles that signify unique roles and responsibilities. These ranks and titles are often associated with specific positions or duties within the military, reflecting the diverse and dynamic nature of military operations. Special ranks and titles provide recognition for individuals who perform critical and specialized roles, contributing to the overall success of the military.
Special ranks and titles may include positions such as command sergeant major, first sergeant, or sergeant major, which denote senior enlisted leadership roles within military units. These positions carry significant authority and responsibility, as they are tasked with overseeing the welfare and discipline of enlisted personnel and ensuring that military standards are upheld. Special ranks and titles may also include positions such as adjutant, quartermaster, or chaplain, which reflect specialized roles and duties within the military.
The path to obtaining a special rank or title involves a combination of experience, training, and demonstrated proficiency in a particular area. Special ranks and titles are often awarded based on an individual's ability to contribute to the success of military operations and their commitment to the values and priorities of the military. By understanding the role of special ranks and titles, we gain insight into the diverse and dynamic nature of military operations and the unique contributions of individuals within the military.
Understanding Insignia and Symbols
Insignia and symbols play a crucial role in the military, serving as visual representations of rank, authority, and affiliation. They provide a clear and concise way to identify the roles and responsibilities of service members within the military hierarchy. Insignia and symbols are worn on uniforms and equipment, allowing service members to quickly and easily identify one another's rank and position.
Each rank within the military has its own distinct insignia, which typically includes a combination of symbols, stripes, and stars. These insignia are worn on uniforms and represent the level of authority and responsibility associated with the rank. In addition to rank insignia, there are also unit insignia and patches that denote affiliation with specific units or branches of the military. These symbols reflect the pride and tradition of military service and serve as a reminder of the shared mission and values of the military.
Understanding insignia and symbols is essential for anyone interacting with military personnel, as it provides insight into the roles and responsibilities of service members. It also fosters a greater appreciation for the dedication and commitment of those who serve. By examining the various insignia and symbols used within the military, we gain a deeper understanding of the visual language and culture of military service.
The Role of Military Education and Training
Military education and training play a vital role in preparing service members for the demands of military service and ensuring that they are equipped with the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed. Education and training programs are designed to develop leadership, technical proficiency, and professional competence, providing service members with the tools they need to perform their duties effectively.
Military education and training encompass a wide range of programs and opportunities, from basic training for new recruits to advanced leadership courses for senior officers. These programs focus on developing critical skills such as leadership, communication, decision-making, and technical proficiency. They also emphasize the importance of teamwork, discipline, and adherence to military values and standards.
The path to advancement within the military often involves completing specific education and training requirements, which are designed to prepare service members for increased responsibilities and leadership roles. By understanding the role of military education and training, we gain insight into the professional development and growth opportunities available to service members, as well as the commitment to excellence that is a hallmark of military service.
The Path to Promotion: Advancing Through the Ranks
Advancement through the ranks is a key aspect of military service, providing service members with opportunities for increased responsibility, leadership, and professional development. The path to promotion is based on a combination of experience, performance, education, and demonstrated leadership ability. Service members are evaluated regularly and promoted based on their ability to meet the standards and expectations of their rank.
The process of promotion varies depending on the branch of service and the rank in question, but it typically involves a combination of written exams, performance evaluations, and leadership assessments. Service members are expected to demonstrate proficiency in their duties, as well as a commitment to the values and priorities of the military. They are also encouraged to pursue education and training opportunities to enhance their skills and knowledge.
The path to promotion is not without its challenges, as service members must navigate the demands of military service while striving to meet the requirements for advancement. However, it also offers significant rewards, including increased authority, responsibility, and the opportunity to make a meaningful impact within the military. By understanding the path to promotion, we gain insight into the dedication and commitment required to advance through the ranks and the opportunities for growth and leadership within the military.
The Importance of Leadership in the Military
Leadership is a cornerstone of military service, playing a critical role in the success of military operations and the effectiveness of military units. Effective leadership is essential for maintaining discipline, morale, and cohesion within military units, as well as for ensuring that missions are executed successfully and efficiently. Leadership is also crucial for fostering a positive and inclusive command climate, where service members feel valued, respected, and motivated to perform their best.
Military leaders are expected to exhibit a wide range of skills and qualities, including communication, decision-making, adaptability, and integrity. They are also expected to lead by example, demonstrating the values and professionalism expected of military personnel. Military leaders are responsible for developing and mentoring their subordinates, guiding them through the challenges of military service and preparing them for increased responsibilities and leadership roles.
The importance of leadership in the military cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the success and effectiveness of military operations. By understanding the role of leadership in the military, we gain insight into the qualities and skills required to lead effectively and the impact that strong leadership can have on the success and well-being of military personnel.
Comparing Army Ranks Globally
While the structure of army ranks is generally consistent across different countries, there are variations in the specific ranks and titles used by different military forces. These variations reflect the unique history, culture, and priorities of each country's military. By comparing army ranks globally, we gain insight into the similarities and differences between different military forces and the diverse ways in which military operations are organized and executed.
In many countries, the rank structure is divided into similar categories, including enlisted ranks, non-commissioned officers, warrant officers, commissioned officers, and general officers. However, the specific titles and symbols used for each rank may vary. For example, the rank of sergeant may be referred to as "Unteroffizier" in the German military or "sergent" in the French military. Similarly, the rank insignia may differ, with some countries using stars, stripes, or other symbols to denote rank.
Despite these variations, there are many similarities in the roles and responsibilities associated with each rank, as well as the values and priorities that guide military service. By understanding the global context of army ranks, we gain a deeper appreciation for the shared mission and values of military personnel worldwide and the diverse ways in which military operations are conducted.
FAQs About Army Ranks
- What is the lowest rank in the army?
The lowest rank in the army is typically the entry-level enlisted rank, such as Private or its equivalent, depending on the country's military structure.
- How long does it take to advance through the ranks in the army?
The time it takes to advance through the ranks varies based on performance, experience, and completion of required training and education. Promotion timelines are also influenced by the needs of the military and availability of positions.
- What is the difference between commissioned and non-commissioned officers?
Commissioned officers are leaders and commanders responsible for planning and executing military operations, while non-commissioned officers (NCOs) provide guidance and leadership to enlisted personnel and bridge the gap between enlisted personnel and officers.
- Are warrant officers considered commissioned officers?
Warrant officers are a unique category within the military rank structure, serving as technical experts and specialists. They are not typically considered commissioned officers, but they hold positions of authority and responsibility within their areas of expertise.
- How do military ranks differ between countries?
While the general structure of military ranks is similar across countries, the specific titles and insignia may vary. These differences reflect the unique history, culture, and priorities of each country's military.
- What factors influence promotion in the army?
Promotion in the army is influenced by factors such as performance, experience, education, and demonstrated leadership ability. Service members are evaluated regularly and promoted based on their ability to meet the standards and expectations of their rank.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Military Ranks
The military rank structure is a cornerstone of military organization, discipline, and leadership. It provides a framework for command and control, ensuring that military operations are executed effectively and efficiently. Each rank carries its own responsibilities, expectations, and privileges, reflecting the values and priorities of the military as a whole.
Understanding army ranks in order provides insight into the complex and dynamic nature of military service, as well as the dedication and commitment required of those who serve. It highlights the diverse roles and responsibilities of service members, from the junior enlisted personnel to the highest generals, and the critical contributions they make to national security and defense.
The legacy of military ranks is one of tradition, excellence, and professionalism. It is a testament to the enduring values and principles that guide military service, as well as the unwavering commitment of service members to serve and protect their country. As we continue to explore and understand the military rank structure, we gain a deeper appreciation for the sacrifices and achievements of those who have served and continue to serve in the armed forces.
External Resources and Further Reading
For more information on army ranks and military structure, you may refer to the following resources: