Have you ever wondered what melanoma symptoms look like and how they can affect your health? Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that develops in the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives your skin its color. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of melanoma early on is crucial, as it can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment. With skin cancer being one of the most prevalent forms of cancer globally, understanding melanoma symptoms is essential for everyone.
Being informed about melanoma symptoms not only helps in early detection but also empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward their health. Whether it's a new mole, a change in an existing mole, or an unusual growth on your skin, knowing what to look for can make all the difference. This guide will delve into the various symptoms of melanoma, offering insights backed by research and expert opinions. We'll explore the risk factors, diagnostic procedures, and preventive measures to equip you with a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
The journey to understanding melanoma symptoms is not just about identifying potential health concerns but also about fostering awareness and encouraging preventive care. As we navigate through this topic, we'll emphasize the importance of regular skin checks, professional screenings, and the role of lifestyle choices in mitigating risks. By the end of this article, you'll have a well-rounded view of melanoma symptoms, empowering you to make informed decisions about your skin health.
- What is Melanoma?
- The Biology of Melanoma
- Common Melanoma Symptoms
- Early Warning Signs of Melanoma
- Advanced Melanoma Symptoms
- Risk Factors for Melanoma
- The ABCDEs of Melanoma Detection
- How Melanoma is Diagnosed
- Preventive Measures Against Melanoma
- The Role of Genetics in Melanoma
- Melanoma Treatment Options
- Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Melanoma Risk
- Melanoma in Different Skin Types
- Frequently Asked Questions About Melanoma
- Conclusion: Staying Vigilant Against Melanoma
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that originates in the melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, which gives skin its color. Unlike other forms of skin cancer, melanoma is more likely to spread to other parts of the body if not detected early. While it accounts for a small percentage of skin cancer cases, it is the most dangerous due to its aggressive nature and potential to metastasize.
Understanding melanoma requires a look at how it develops. Typically, melanoma begins on the skin as a new spot or a change in an existing mole. It can appear anywhere on the body but is most commonly found on areas exposed to the sun, such as the back, legs, arms, and face. However, it can also develop in less obvious places like the soles of the feet, palms, and even under the nails.
Despite its severity, melanoma can be effectively treated if caught early. This is why awareness and education about melanoma symptoms are crucial. By recognizing the signs of melanoma and understanding the risk factors, individuals can seek medical attention promptly and improve their prognosis.
The Biology of Melanoma
Melanoma begins in the pigment-producing melanocytes located in the basal layer of the epidermis. These cells produce melanin, which helps protect the skin from ultraviolet (UV) radiation. However, when these cells undergo genetic mutations, they can grow uncontrollably, leading to melanoma.
The mutation process is often triggered by DNA damage caused by UV radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. This damage can lead to abnormal cell behavior, causing melanocytes to multiply rapidly and form malignant tumors. Over time, these cancerous cells can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system or bloodstream.
Understanding the biological underpinnings of melanoma helps in developing targeted treatments and preventive measures. Researchers continue to study the genetic mutations associated with melanoma to identify potential therapeutic targets and improve patient outcomes.
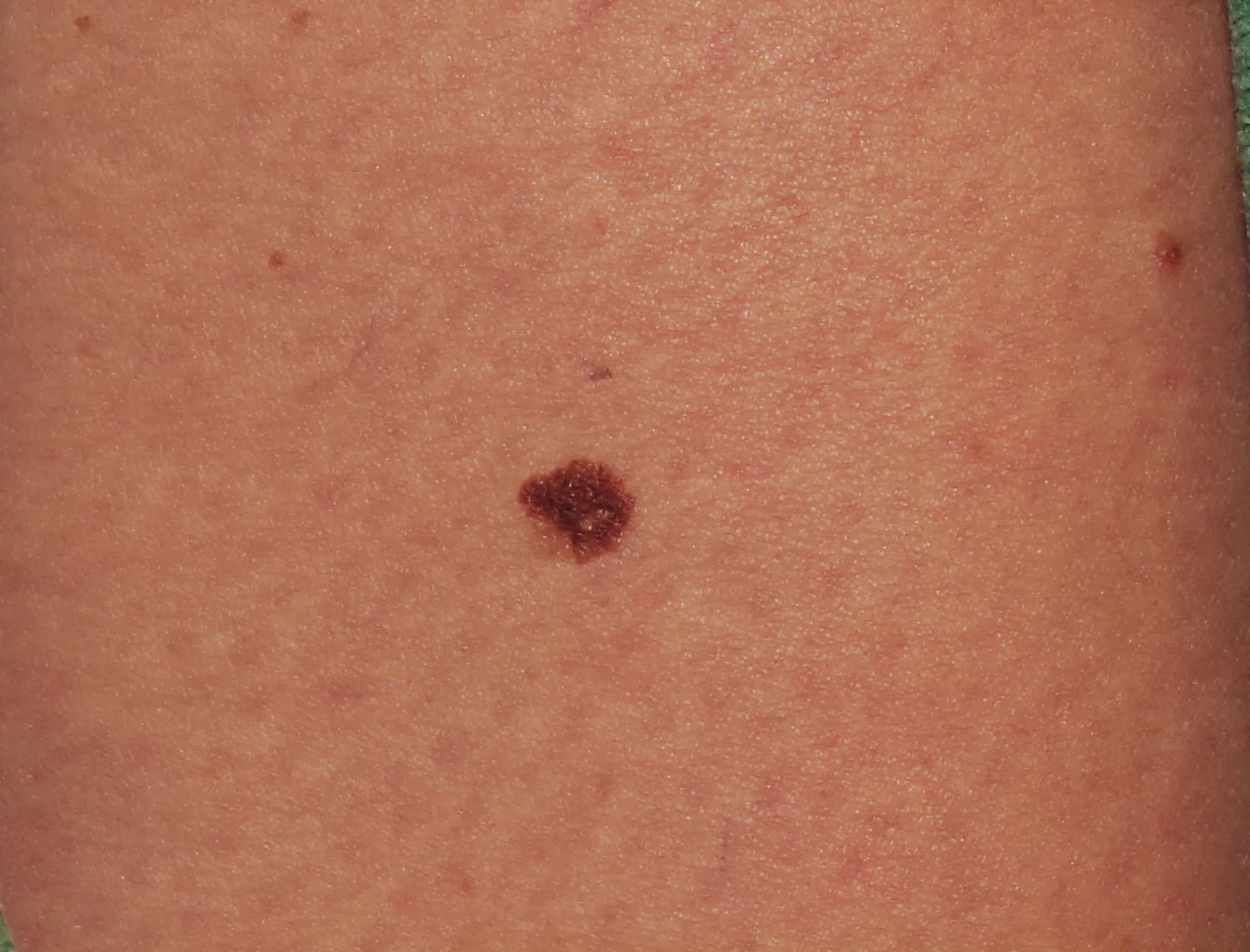
Common Melanoma Symptoms
Recognizing common melanoma symptoms is vital for early detection and treatment. Melanoma often presents itself as a change in an existing mole or the appearance of a new, unusual-looking mole. Here are some typical symptoms to watch out for:
- Asymmetry: Unlike normal moles, melanomas are often asymmetrical. If you draw a line through the middle of a mole, the two halves will not match.
- Border Irregularity: Melanomas tend to have uneven or notched borders, unlike the smooth, even borders of benign moles.
- Color Variation: Look for moles with multiple colors such as shades of brown, black, blue, red, or white.
- Diameter: Melanomas are usually larger than 6 millimeters, approximately the size of a pencil eraser, but can be smaller when first detected.
- Evolution: Any change in size, shape, color, or elevation of a mole, or new symptoms such as bleeding, itching, or crusting, should raise concerns.
Being aware of these symptoms is critical, but it's also important to remember that not all melanomas fit these criteria. Some may appear as a new spot that doesn't look like any other spot on your body. If you notice any suspicious changes, it's essential to consult a dermatologist for a professional evaluation.
Early Warning Signs of Melanoma
Early detection of melanoma significantly improves the chances of successful treatment. Therefore, understanding the early warning signs is crucial. One of the most recognized methods for identifying potential melanomas is the ABCDE rule, which stands for Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, and Evolution. However, there are additional signs to be mindful of:
- The Ugly Duckling Sign: This refers to a mole that looks different from the other moles on your body. It may be larger, darker, or have an unusual shape.
- New Growths: Be vigilant about new growths on your skin, especially if they appear suddenly and stand out compared to other moles.
- Non-Healing Sores: A sore that doesn't heal or one that heals and then reopens can be a sign of skin cancer.
- Changes in Sensation: If you experience itching, tenderness, or pain in a mole or spot on your skin, it warrants a closer look.
These early signs serve as red flags that should prompt further investigation. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks are invaluable in catching melanoma in its early stages when treatment is most effective.
Advanced Melanoma Symptoms
When melanoma progresses beyond the early stages, it can lead to more severe symptoms as the cancer spreads to other parts of the body. Advanced melanoma symptoms may include:
- Persistent Swelling: Swollen lymph nodes, especially near the area of the melanoma, can indicate that cancer has spread.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: As with many cancers, weight loss without a clear reason can be a symptom of advanced melanoma.
- Fatigue: Persistent, unexplained fatigue is a common symptom as the body fights the spread of cancer.
- Breathing Difficulties: If melanoma spreads to the lungs, it can cause shortness of breath or a persistent cough.
- Pain: Pain in bones or other areas of the body can occur if melanoma spreads beyond the skin.
These advanced symptoms highlight the importance of early detection and regular monitoring. Melanoma's ability to spread rapidly means that catching it before it progresses can dramatically affect treatment options and outcomes.
Risk Factors for Melanoma
Understanding the risk factors for melanoma can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and take preventive measures. Key risk factors include:
- Exposure to UV Radiation: Prolonged exposure to the sun's UV rays and artificial sources like tanning beds increases melanoma risk.
- Fair Skin: Individuals with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes have less melanin, offering less protection against UV radiation.
- Family History of Melanoma: A family history of melanoma indicates a genetic predisposition to the disease.
- Multiple Moles or Atypical Moles: Having more than 50 moles or atypical moles increases melanoma risk.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions or medications that suppress the immune system can increase vulnerability to melanoma.
By understanding these risk factors, individuals can take steps to mitigate them, such as using sunscreen, avoiding tanning beds, and conducting regular skin checks.
The ABCDEs of Melanoma Detection
The ABCDE rule is a widely recognized method for evaluating moles and skin lesions for signs of melanoma. This guideline helps individuals and healthcare professionals identify potential melanomas early. Here's a breakdown:
- Asymmetry (A): One half of the mole doesn't match the other half.
- Border (B): The edges are irregular, ragged, or blurred.
- Color (C): The color is not uniform and may include shades of brown or black, or sometimes patches of pink, red, white, or blue.
- Diameter (D): The mole is larger than 6 mm, about the size of a pencil eraser, but melanomas can be smaller.
- Evolution (E): Any change in the mole's size, shape, color, elevation, or any new symptom such as bleeding, itching, or crusting.
The ABCDE rule is a straightforward yet effective tool for early melanoma detection. It encourages individuals to be proactive about their skin health and seek medical advice if they notice any suspicious changes.
How Melanoma is Diagnosed
Diagnosing melanoma involves a combination of self-examination, clinical evaluation, and diagnostic tests. The process typically begins with a visual examination by a dermatologist, who will assess any suspicious moles or skin lesions. If a lesion appears concerning, a biopsy is often performed to confirm the diagnosis.
There are several types of biopsies used in diagnosing melanoma, including:
- Excisional Biopsy: The entire mole or suspicious area is removed for analysis.
- Incisional Biopsy: Only a portion of the suspicious area is removed for examination.
- Punch Biopsy: A small, round piece of skin is removed using a punch tool for analysis.
Once the biopsy is performed, the sample is examined under a microscope to determine the presence of cancerous cells. If melanoma is confirmed, additional tests may be conducted to assess the cancer's stage and whether it has spread to other parts of the body.
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, and regular skin examinations by a healthcare professional are recommended for those at higher risk of melanoma.
Preventive Measures Against Melanoma
Preventing melanoma involves a combination of lifestyle choices and protective measures to minimize UV exposure. Key preventive strategies include:
- Using Sunscreen: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days.
- Wearing Protective Clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts, pants, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses to shield your skin from the sun.
- Seeking Shade: Avoid the sun during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.) and seek shade when possible.
- Avoiding Tanning Beds: Refrain from using tanning beds, as they emit harmful UV radiation.
- Regular Skin Checks: Conduct monthly self-examinations and schedule annual check-ups with a dermatologist.
By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing melanoma and other forms of skin cancer.
The Role of Genetics in Melanoma
Genetics play a significant role in melanoma risk, with certain inherited traits and gene mutations increasing susceptibility to the disease. For instance, individuals with a family history of melanoma or certain genetic conditions, such as familial atypical multiple mole and melanoma (FAMMM) syndrome, are at a higher risk.
Research has identified specific gene mutations, such as those in the CDKN2A and BRAF genes, that are linked to melanoma. These genetic markers can provide insight into an individual's predisposition to the disease and guide personalized prevention and treatment strategies.
Genetic counseling and testing can be beneficial for those with a family history of melanoma, allowing for proactive monitoring and early intervention. Understanding the genetic factors involved in melanoma can also inform decisions about lifestyle changes and preventive measures.
Melanoma Treatment Options
Treatment options for melanoma depend on the stage of the cancer, its location, and the patient's overall health. Common treatment modalities include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the melanoma and surrounding tissue is the primary treatment for early-stage melanoma.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment boosts the body's immune system to fight cancer cells more effectively.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs targeting specific genetic mutations in melanoma cells are used to inhibit cancer growth.
- Chemotherapy: Although less commonly used, chemotherapy can be effective for advanced melanoma that has spread.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays are used to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors, often used for melanoma that has spread to other organs.
The choice of treatment is tailored to the individual's specific circumstances and may involve a combination of therapies. Early-stage melanoma has a high cure rate with surgical intervention, while advanced melanoma may require more aggressive treatments.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Melanoma Risk
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to reducing the risk of melanoma. Key lifestyle changes include:
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants can support skin health and overall well-being.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity boosts the immune system and aids in maintaining a healthy weight.
- Avoiding Smoking: Smoking can impair the immune system and increase the risk of various cancers, including skin cancer.
- Limiting Alcohol Consumption: Reducing alcohol intake can lower the risk of certain cancers.
- Stress Management: Practicing stress-reduction techniques like meditation and yoga can improve overall health and resilience.
These lifestyle changes, combined with protective measures against UV exposure, create a comprehensive approach to reducing melanoma risk and promoting long-term health.
Melanoma in Different Skin Types
Melanoma can affect individuals of all skin types, but the presentation and risk factors may vary. People with fair skin are more susceptible to melanoma due to lower melanin levels, which provide less natural protection against UV radiation. However, individuals with darker skin are not immune and may experience melanoma in less visible areas, such as the palms, soles, or under the nails.
Regardless of skin type, it's important to conduct regular skin checks and be aware of any changes. For those with darker skin, paying attention to less common areas and understanding that melanoma can occur in different forms are crucial for early detection and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions About Melanoma
1. Can melanoma occur without sun exposure?
Yes, while UV exposure is a significant risk factor, melanoma can develop in areas not typically exposed to the sun, indicating that other factors, including genetics, can contribute to its occurrence.
2. How often should I check my skin for melanoma symptoms?
It's recommended to perform self-examinations once a month and have a professional skin check annually, or more frequently if you have risk factors for melanoma.
3. Are there any effective natural remedies for treating melanoma?
While some natural remedies may support overall health, there is no scientific evidence that they can treat melanoma. It's crucial to seek professional medical treatment for melanoma.
4. Can children develop melanoma?
Although rare, melanoma can occur in children. It's essential to protect children's skin from UV exposure and be aware of any unusual skin changes.
5. What should I do if I notice a suspicious mole?
If you notice any changes in a mole or spot on your skin, consult a dermatologist promptly for a professional evaluation and possible biopsy.
6. Does having a tan protect against melanoma?
No, a tan is a sign of skin damage and does not protect against melanoma. It's important to use sunscreen and other protective measures to reduce risk.
Conclusion: Staying Vigilant Against Melanoma
Understanding melanoma symptoms is a vital part of protecting your health and well-being. By recognizing the signs and taking preventive measures, you can reduce your risk and catch melanoma early when it's most treatable. Regular skin checks, both self-examinations and professional evaluations, are essential components of a proactive approach to skin health.
Stay informed about the risk factors, be vigilant about changes in your skin, and adopt a lifestyle that supports overall health. With knowledge and awareness, you can play an active role in preventing melanoma and ensuring a healthy future.
For more information on skin cancer and related topics, please visit the American Cancer Society.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-melanoma-514215_final-01-3b091d9a68074ba7b5a1cb6d8287cf92.png)